Google Cloud Realtime Database#
The Google Cloud Realtime Database node allows you to automate work in Google Cloud Realtime Database, and integrate Google Cloud Realtime Database with other applications. n8n has built-in support for a wide range of Google Cloud Realtime Database features, including writing, deleting, getting, and appending databases.
On this page, you'll find a list of operations the Google Cloud Realtime Database node supports and links to more resources.
Credentials
Refer to Google Cloud Realtime Database credentials for guidance on setting up authentication.
Examples and templates
For usage examples and templates to help you get started, take a look at n8n's Google Cloud Realtime Database integrations list.
Basic Operations#
- Write data to a database
- Delete data from a database
- Get a record from a database
- Append to a list of data
- Update item on a database
Example Usage#
This workflow allows you to receive updates of the position of the ISS every minute and push it to a database using the Google Cloud Realtime Database node. You can also find the workflow on n8n.io. This example usage workflow uses the following nodes.
The final workflow should look like the following image.
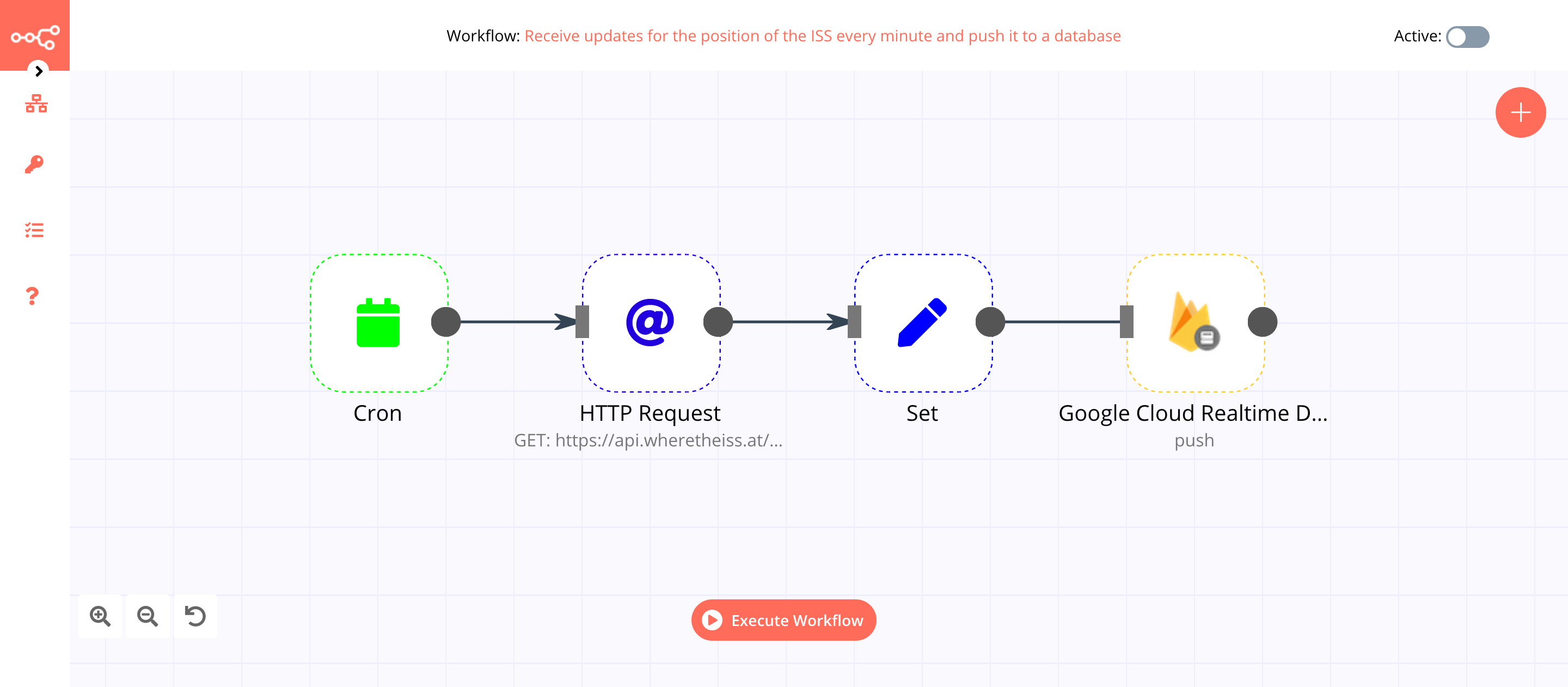
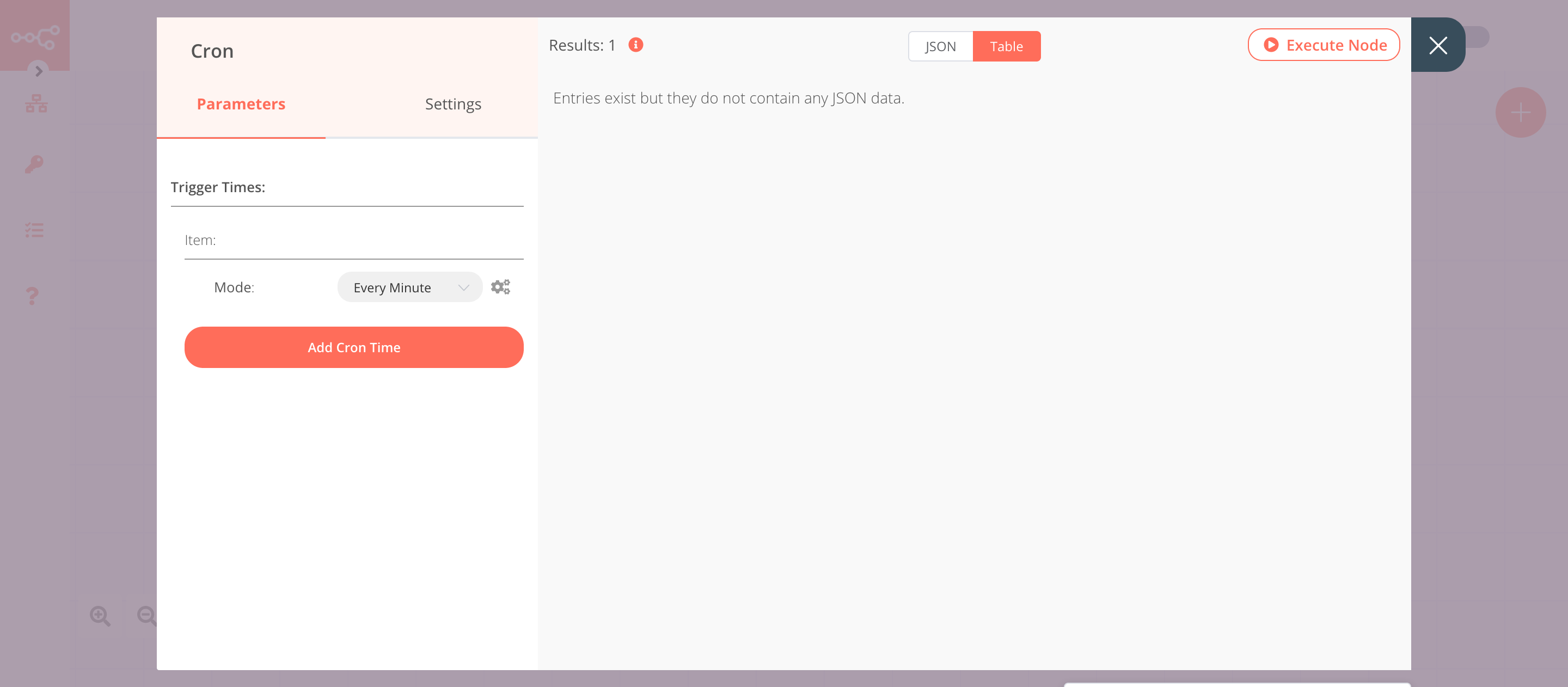
1. Cron node#
The Cron node will trigger the workflow every minute.
- Click on Add Cron Time.
- Select 'Every Minute' from the Mode dropdown list.
- Click on Execute Node to run the node.
In the screenshot below, you will notice that the Cron node is configured to trigger the workflow every minute.
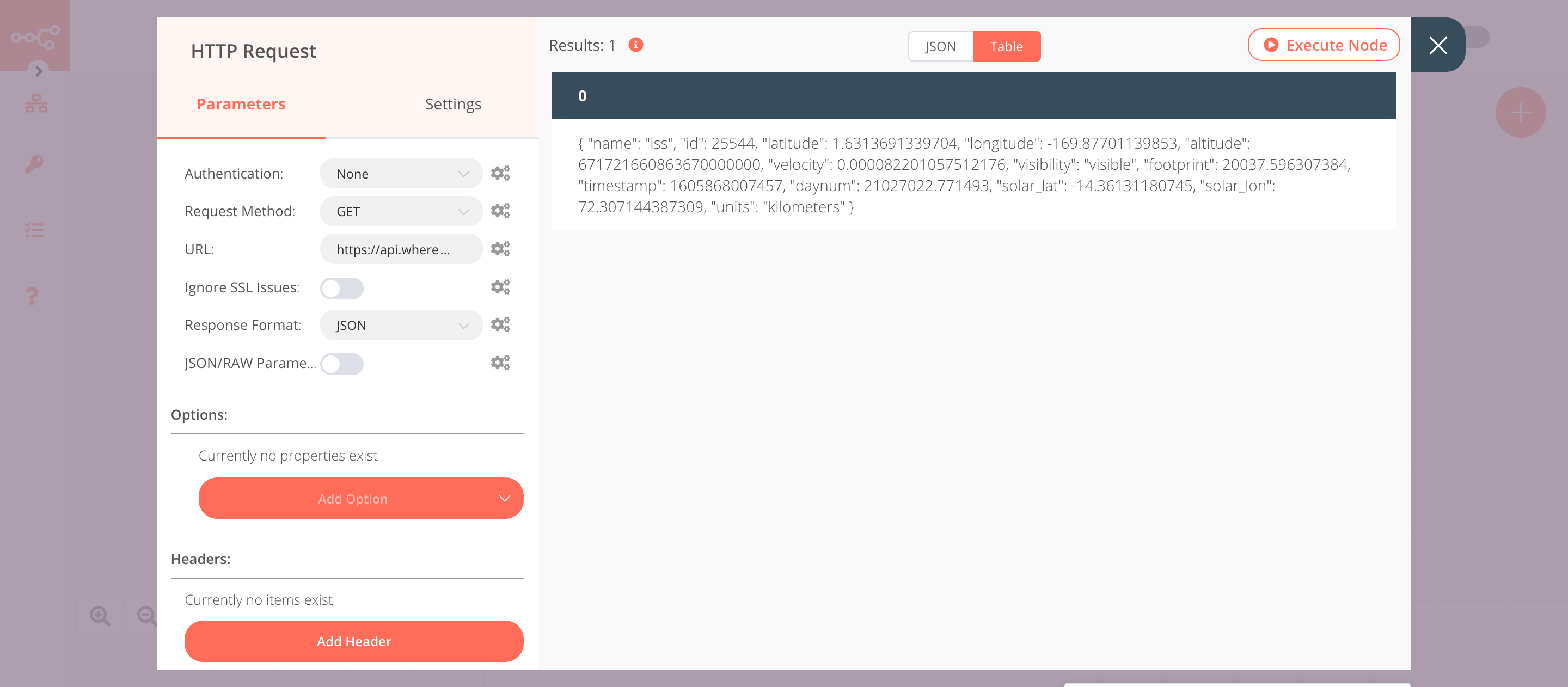
2. HTTP Request node (GET)#
This node will make a GET request to the API https://api.wheretheiss.at/v1/satellites/25544/positions to fetch the position of the ISS. This information gets passed on to the next node in the workflow.
- Enter
https://api.wheretheiss.at/v1/satellites/25544/positionsin the URL field. - Click on the Add Parameter button in the Query Parameters section.
- Enter
timestampsin the Name field. - Click on the gears icon next to the Value field and click on Add Expression.
- Enter the following expression:
{{Date.now()}}. This expression will return the current timestamp. - Click on Execute Node to run the node.
In the screenshot below, you will notice that the node makes a GET request to the API and returns the information about the location of the ISS.
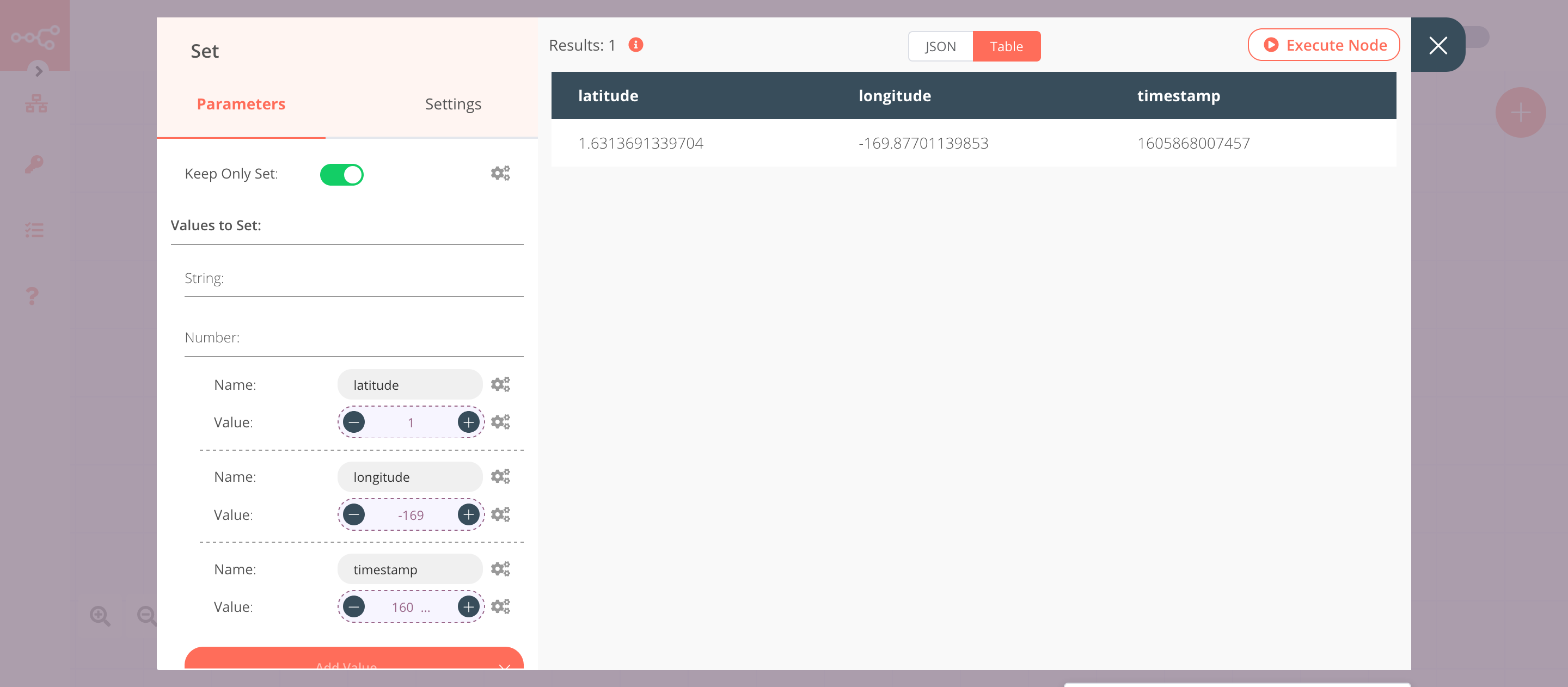
3. Set node#
We will use the Set node to ensure that only the data that we set in this node gets passed on to the next nodes in the workflow.
- Click on Add Value and select 'String' from the dropdown list.
- Enter
latitudein the Name field. - Click on the gears icon next to the Value field and click on Add Expression.
- Select the following in the Variable Selector section: Nodes > HTTP Request > Output Data > JSON > 0 > latitude. You can also add the following expression:
{{$node["HTTP Request"].json["0"]["latitude"]}}. - Click on Add Value and select 'String' from the dropdown list.
- Enter
longitudein the Name field. - Click on the gears icon next to the Value field and click on Add Expression.
- Select the following in the Variable Selector section: Nodes > HTTP Request > Output Data > JSON > 0 > longitude. You can also add the following expression:
{{$node["HTTP Request"].json["0"]["longitude"]}}. - Click on Add Value and select 'String' from the dropdown list.
- Enter
timestampin the Name field. - Click on the gears icon next to the Value field and click on Add Expression.
- Select the following in the Variable Selector section: Nodes > HTTP Request > Output Data > JSON > 0 > timpestamp. You can also add the following expression:
{{$node["HTTP Request"].json["0"]["timestamp"]}}. - Toggle Keep Only Set to
true. We set this option to true to ensure that only the data that we have set in this node get passed on to the next nodes in the workflow. - Click on Execute Node to run the node.
In the screenshot below, you will notice that the node uses the data from the previous node and returns the data that we set for the workflow.
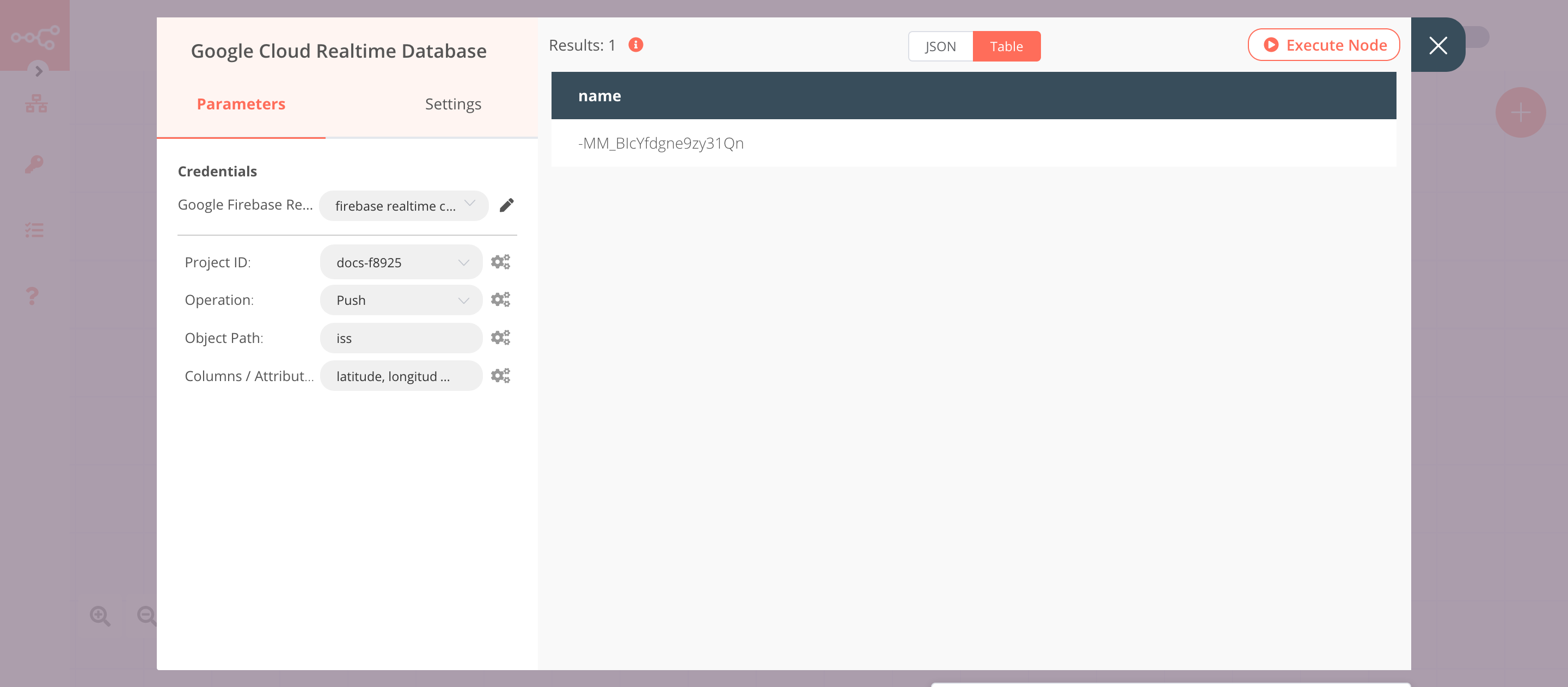
4. Google Cloud Realtime Database node (push)#
This node will push the data from the previous node to the iss path in Google Cloud Realtime Database. If you have created a path with a different name, you can use that path instead.
- First of all, you'll have to enter credentials for the Google Cloud Realtime Database node. You can find out how to do that here.
- Select a project from the Project ID dropdown list.
- Select 'Push' from the Operation dropdown list.
- Enter a path in the Object Path field.
- Enter
latitude, longitude, timestampin the Columns / Attributes field. - Click on Execute Node to run the node.
In the screenshot below, you will notice that the node pushes the data from the previous node to the iss path in Google Cloud Realtime Database.
Activate workflow for production
This example workflow uses the Cron node, which is a Trigger node. You'll need to save the workflow and then click on the Activate toggle on the top right of the screen to activate the workflow. Your workflow will then be triggered as specified by the settings in the Cron node.